The perivascular hypodense rim in carotid body tumor surgery

| Available Online: | January, 2024 |
| Page: | 29-30 |
Author for correspondence:
Mila Evaggelia
Vascular Surgery Department, Patras University Hospital, 26504, Rio, Patras Greece
E-mail: meva713@gmail.com
doi: 10.59037/fmn9jm44
ISSN 2732-7175 / 2024 Hellenic Society of Vascular and Endovascular Surgery Published by Rotonda Publications All rights reserved. https://www.heljves.com
Full Text
References
Images
Full Text
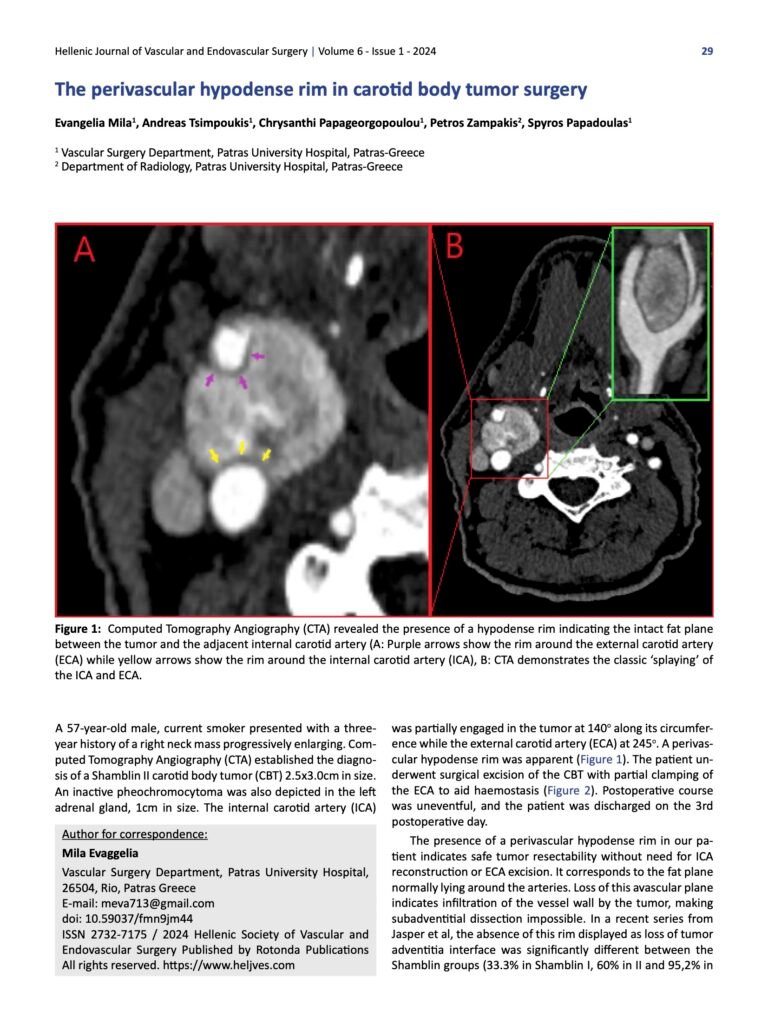
Figure 1: Computed Tomography Angiography (CTA) revealed the presence of a hypodense rim indicating the intact fat plane between the tumor and the adjacent internal carotid artery (A: Purple arrows show the rim around the external carotid artery (ECA) while yellow arrows show the rim around the internal carotid artery (ICA), B: CTA demonstrates the classic ‘splaying’ of the ICA and ECA.
A 57-year-old male, current smoker presented with a three-year history of a right neck mass progressively enlarging. Computed Tomography Angiography (CTA) established the diagnosis of a Shamblin II carotid body tumor (CBT) 2.5×3.0cm in size. An inactive pheochromocytoma was also depicted in the left adrenal gland, 1cm in size. The internal carotid artery (ICA) was partially engaged in the tumor at 140o along its circumference while the external carotid artery (ECA) at 245o. A perivascular hypodense rim was apparent (Figure 1). The patient underwent surgical excision of the CBT with partial clamping of the ECA to aid haemostasis (Figure 2). Postoperative course was uneventful, and the patient was discharged on the 3rd postoperative day.
The presence of a perivascular hypodense rim in our patient indicates safe tumor resectability without need for ICA reconstruction or ECA excision. It corresponds to the fat plane normally lying around the arteries. Loss of this avascular plane indicates infiltration of the vessel wall by the tumor, making subadventitial dissection impossible. In a recent series from Jasper et al, the absence of this rim displayed as loss of tumor adventitia interface was significantly different between the Shamblin groups (33.3% in Shamblin I, 60% in II and 95,2% in III)1. Consequently, lack of this radiological sign increases the likelihood for tumor adherence to ICA needing arterial reconstruction and higher morbidity is anticipated (e.g., strokes and cranial nerve palsies).
Figure 2: Intraoperative photos, A: The tumor was dissected free from the internal carotid artery (ICA) through a subadventitial avascular plane (Orange arrow: ICA, light green arrow: superior thyroid artery), B: Partial external carotid artery (ECA) clamping was performed (Blue arrow),(Light blue arrow: the hypoglossal nerve) C: Carotid bifurcation after tumor excision (Green arrow: Common carotid artery, orange arrow: ICA, blue arrow: ECA, light blue arrow: the hypoglossal nerve ), D: The excised carotid body tumor
References
- Jasper A, Mammen S, Gowri MS, Keshava SN, Selvaraj D. Imaging criteria to predict Shamblin group in carotid body tumors – revisited. Diagn Interv Radiol. 2021 May;27(3):354-359.